Submitting your sitemap to search engines is a crucial step in ensuring your website gets properly indexed and ranks well in search results.
This detailed guide will walk you through the process for all major search engines, helping you maximize your site’s visibility online.
What is a Sitemap and Why Is It Important?
A sitemap is essentially a blueprint of your website that lists all its pages in a structured format (typically XML). This file provides search engines with organized information about the pages, videos, and other files on your site, including data about each item’s relative importance and how often it’s updated.
Benefits of Using Sitemaps:
- Enhanced Discoverability: Search engines can find new or updated content much faster
- Improved Crawl Efficiency: Helps search engines prioritize which pages to crawl first
- Better Indexing Coverage: Ensures important pages aren’t missed during crawling
- Mobile and Multimedia Support: Modern sitemaps can include specific information for mobile pages, videos, images, and news content
- Analytics Insights: After submission, you can monitor how search engines interact with your content
Preparing Your Sitemap
Before submission, ensure your sitemap is:
- Up-to-date: Reflecting your current site structure
- Properly formatted: Valid XML that adheres to the sitemap protocol
- Reasonably sized: Under 50MB and containing fewer than 50,000 URLs (split into multiple sitemaps if needed)
- Accessible: Located in your site’s root directory or properly referenced in your robots.txt file
Many CMS platforms like WordPress automatically generate sitemaps, or you can use dedicated plugins like Yoast SEO or specialized sitemap generators.
Submitting Your Sitemap to Google
1) Access Google Search Console
Start by navigating to Google Search Console and logging into your Google account. If you haven’t yet set up Search Console for your website, you’ll need to add your property and verify ownership through one of several methods:
- HTML file upload
- HTML tag
- DNS record
- Google Analytics connection
- Google Tag Manager connection
2) Select Your Website Property
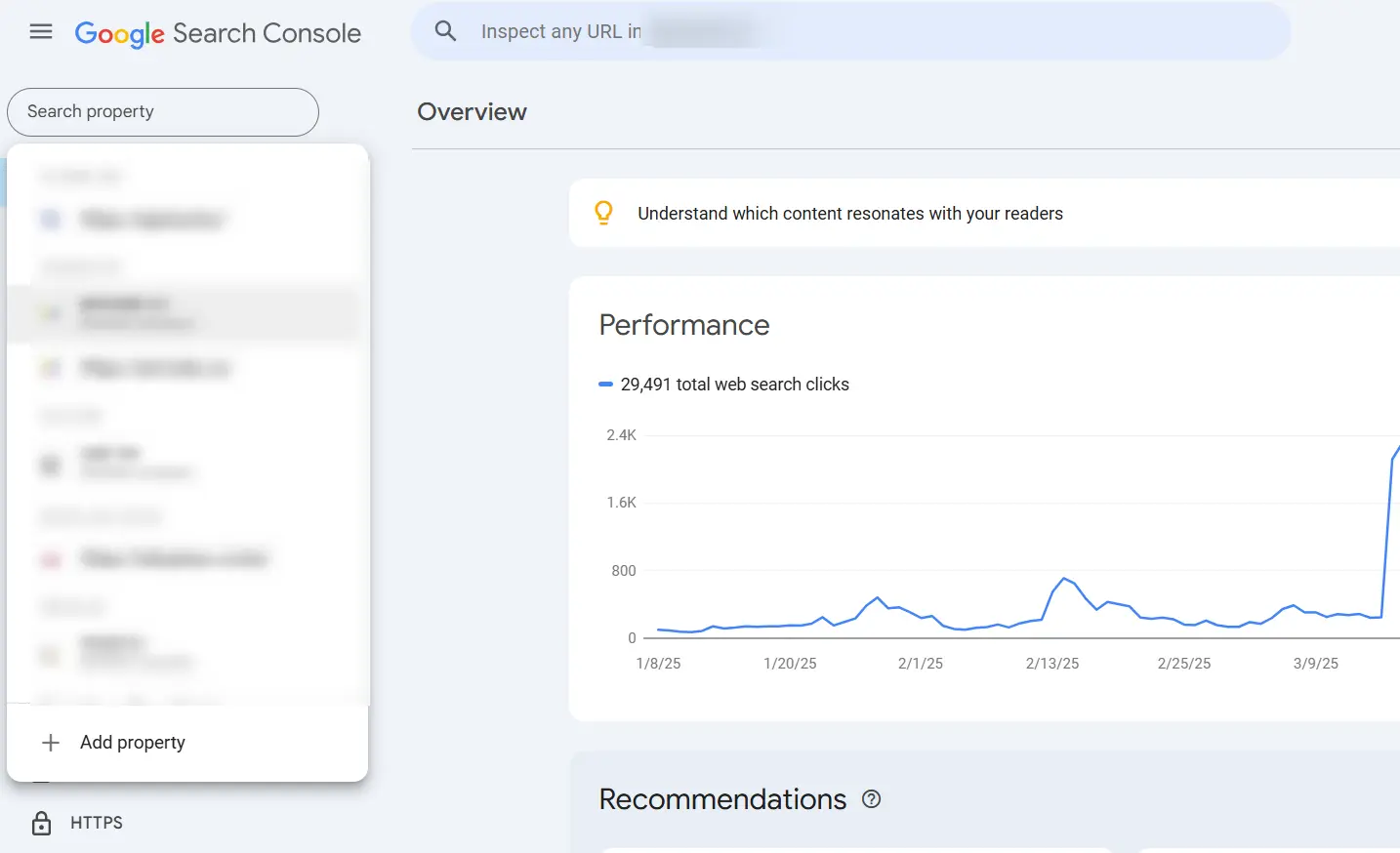
Once logged in, select the appropriate property from the dropdown menu at the top of the page. Ensure you’re working with the correct version of your site (https vs. http, www vs. non-www).
3) Go to the Sitemaps Section
In the left-hand navigation menu, locate and click on “Sitemaps” under the “Index” section.
This will take you to the sitemap management interface.
4) Submit Your Sitemap URL
In the “Add a new sitemap” field at the top of the page, enter the relative URL of your sitemap (e.g., sitemap.xml or sitemap_index.xml).
If you have multiple sitemaps, you can submit them individually or submit a sitemap index file that references all your individual sitemaps.
5) Click “Submit” and Verify
After clicking the “Submit” button, Google will process your sitemap.
This typically happens quickly, but complete crawling may take some time depending on your site’s size.
6) Monitor Status and Address Issues
Once processed, your sitemap will appear in the list with status information, including:
- The number of URLs submitted
- The number of URLs indexed
- Any warnings or errors discovered
If errors are found, click on the sitemap to view detailed information and address the issues before resubmitting.
Submitting Your Sitemap to Bing
Bing powers not only its own search results but also Yahoo’s, making this submission particularly valuable.
1) Create a Bing Webmaster Tools Account
Visit Bing Webmaster Tools and sign in with your Microsoft account. If you don’t have one, you’ll need to create it.
2) Add and Verify Your Website
Click on “Add your site” and enter your website’s URL. Bing will then require verification of ownership through one of several methods:
- XML file authentication
- Meta tag verification
- DNS verification
- Adding a CNAME record
3) Access the Sitemaps Tool
Once your site is verified, navigate to the “Sitemaps” section from the left sidebar menu.
4) Add Your Sitemap
Enter the complete URL of your sitemap (e.g., https://yourwebsite.com/sitemap.xml) in the input field and click “Submit.”
5) Review Status and Performance
Bing Webmaster Tools provides detailed reports on how your sitemap is performing, including:
- Submission status
- Crawl statistics
- Index coverage
- Any errors or warnings that need attention
6) Set Up Regular Crawling (Optional)
Bing allows you to adjust crawl settings to ensure regular updates. Navigate to the “Crawl Control” section to customize how often Bing crawls your site.
Submitting Your Sitemap to Yandex
Yandex is particularly important if you target audiences in Russia and Eastern Europe.
i) Create a Yandex Webmaster Account
Visit Yandex Webmaster and sign in with your Yandex account. Create one if necessary.
ii) Add Your Website
Click on “Add site” and enter your website’s URL. Verify ownership through one of the provided methods:
- HTML file
- Meta tag
- DNS record
- HTML tag
iii) Navigate to Sitemap Settings
Once verified, find the “Indexing” section in the left menu and select “Sitemaps.”
iv) Add Your Sitemap
Enter the full URL of your sitemap in the designated field and click “Add.”
v) Monitor Indexing Progress
Yandex provides detailed information about:
- Sitemap processing status
- URLs discovered and indexed
- Error reports and recommendations
vi) Address Geographic Targeting (Optional)
If your site targets specific regions, use the “Regional preferences” section to specify your geographic targeting, which can improve relevance for searches from those regions.
Optimizing for DuckDuckGo
DuckDuckGo operates differently from other search engines as it doesn’t have a direct sitemap submission process.
However, you can optimize for DuckDuckGo through these steps:
I) Focus on Bing Optimization
DuckDuckGo pulls results from multiple sources, with Bing being a primary source.
By submitting your sitemap to Bing, you’re indirectly optimizing for DuckDuckGo as well.
ii) Ensure Proper robots.txt Configuration
Make sure your robots.txt file correctly references your sitemap:
Sitemap: https://yourwebsite.com/sitemap.xmliii) Implement Privacy-Focused SEO
Since DuckDuckGo emphasizes privacy, ensure your site:
- Has a clear privacy policy
- Minimizes tracking and cookies
- Uses HTTPS encryption
- Focuses on quality content rather than aggressive tracking techniques
Additional Search Engines to Consider
Baidu (For Chinese Markets)
- Create a Baidu Webmaster Tools account
- Verify your website
- Navigate to the “Sitemaps” section
- Submit your sitemap URL
- Note that Baidu has strict requirements for non-Chinese websites, and verification may take longer
Naver (For South Korean Markets)
- Register with Naver Webmaster Tools
- Verify ownership
- Submit your sitemap in the dedicated section
- Consider adding Korean language support if targeting this market
Maintaining Your Sitemap Strategy
Regular Updates
Update and resubmit your sitemap whenever significant changes occur on your website:
- New sections or pages added
- Content reorganization
- Pages deleted or merged
- URL structure changes
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Regularly check all webmaster tools accounts to:
- Identify crawling errors
- Address indexing issues
- Monitor coverage statistics
- Verify that important pages are being indexed
Using Sitemap Index Files
For larger websites, implement a sitemap index strategy:
- Create individual sitemaps for different sections of your site
- Generate a sitemap index file that references all component sitemaps
- Submit the index file to search engines
- Example structure:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<sitemapindex xmlns="http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9">
<sitemap>
<loc>https://example.com/sitemap-products.xml</loc>
<lastmod>2025-03-01T18:23:17+00:00</lastmod>
</sitemap>
<sitemap>
<loc>https://example.com/sitemap-categories.xml</loc>
<lastmod>2025-03-15T15:30:42+00:00</lastmod>
</sitemap>
<sitemap>
<loc>https://example.com/sitemap-articles.xml</loc>
<lastmod>2025-04-01T12:10:38+00:00</lastmod>
</sitemap>
</sitemapindex>Implementing Special Sitemap Types
Consider specialized sitemaps for specific content types:
- Image Sitemaps: Help search engines discover and index images
- Video Sitemaps: Provide metadata about video content
- News Sitemaps: Specifically for news sites to get content indexed quickly
- Mobile Sitemaps: Indicate mobile-specific content or configurations
Advanced Sitemap Optimization Techniques
Setting Priority and Change Frequency
Within your XML sitemap, use optional attributes to guide search engines:
<priority>: Indicate the relative importance of a page (0.0 to 1.0)<changefreq>: Suggest how often a page changes (hourly, daily, weekly, etc.)<lastmod>: Specify when a page was last modified
Example:
<url>
<loc>https://example.com/important-page/</loc>
<lastmod>2025-04-01T12:30:00+00:00</lastmod>
<changefreq>weekly</changefreq>
<priority>0.8</priority>
</url>Using HTTP Status Codes Correctly
Ensure proper HTTP status codes are implemented:
- 200 OK for accessible pages
- 301 for permanent redirects (update these in your sitemap)
- 404 for removed pages (remove these from your sitemap)
- 410 for permanently deleted content
Conclusion
Submitting your sitemap to search engines is not a one-time task but an ongoing aspect of SEO maintenance.
By following this comprehensive guide, you’ll ensure that search engines can discover, crawl, and index your content efficiently, leading to better visibility in search results across all major platforms.
Remember that while sitemap submission is important, it works best as part of a holistic SEO strategy that includes quality content creation, technical optimization, and user experience improvements. Regularly monitor your webmaster tools accounts to ensure continued optimal performance and address any issues promptly.
 Domain SearchInstantly check and register your preferred domain name
Domain SearchInstantly check and register your preferred domain name Web Hosting
Web Hosting cPanel HostingHosting powered by cPanel (Most user friendly)
cPanel HostingHosting powered by cPanel (Most user friendly) KE Domains
KE Domains Reseller HostingStart your own hosting business without tech hustles
Reseller HostingStart your own hosting business without tech hustles Windows HostingOptimized for Windows-based applications and sites.
Windows HostingOptimized for Windows-based applications and sites. Free Domain
Free Domain Affiliate ProgramEarn commissions by referring customers to our platforms
Affiliate ProgramEarn commissions by referring customers to our platforms Free HostingTest our SSD Hosting for free, for life (1GB storage)
Free HostingTest our SSD Hosting for free, for life (1GB storage) Domain TransferMove your domain to us with zero downtime and full control
Domain TransferMove your domain to us with zero downtime and full control All DomainsBrowse and register domain extensions from around the world
All DomainsBrowse and register domain extensions from around the world .Com Domain
.Com Domain WhoisLook up domain ownership, expiry dates, and registrar information
WhoisLook up domain ownership, expiry dates, and registrar information VPS Hosting
VPS Hosting Managed VPSNon techy? Opt for fully managed VPS server
Managed VPSNon techy? Opt for fully managed VPS server Dedicated ServersEnjoy unmatched power and control with your own physical server.
Dedicated ServersEnjoy unmatched power and control with your own physical server.






